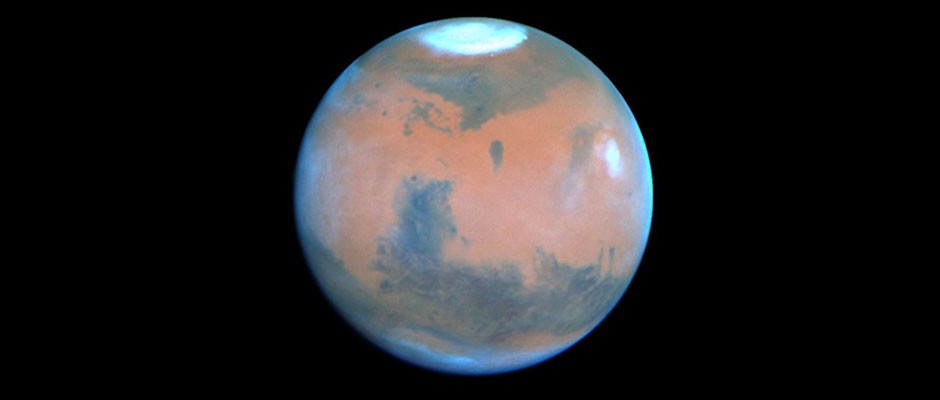

Mars: Oodles of interesting facts, figures and fun questions about the Red Planet
Join us on a journey to the fourth planet from the Sun with amazing facts, incredible images and vital information about Mars.
Our nearest planetary neighbour has been inspiring astronomers, stargazers and those trying to understand night sky for thousands of years, but we are forever learning more about the Red Planet. Who knows, one day we might discover even more by living on it.
Here are the amazing facts about Mars and interesting stats, figures and info you need to get to know the fourth planet from the Sun.
How long does it take to get to Mars?

That depends on when you travel and how you plan on getting there. As the distance between Earth and Mars is constantly changing, so too does the amount of time it takes to get there. The quickest journey to the Red Planet by a spacecraft was Mariner 7's 1969 flyby, which took 128 days to arrive.
How far is Mars from Earth?
Due to their elliptical orbits, the distance between Mars and Earth is always changing as they spin around the Sun. At their closest approach, Mars is only 54.6 million kilometres (33.9 million miles) away. At their furthest, there are some 400 million km (250 million miles) between them.
Read more about human missions to Mars:
- Ingenuity: How the Mars helicopter will fly on another planet
- What Roald Amundsen's polar exploration 'comedian' can teach us about a mission to Mars
- The next great search for life on Mars
How many moons does Mars have?

There are two Mars moons; Phobos and Deimos. Phobos is the larger of the two but it is still tiny, with a radius of around 11km. Both moons were named after the Greek gods (and twin sons of the god Mars) of fear and terror respectively. They were discovered in 1877 by American astronomer Asaph Hall.
How long is a day on Mars?
Mars and Earth have very similar lengths of day. One day on Mars, known as a 'sol', lasts 24 hours, 39 minutes, and 35.244 Earth seconds.
Which country went to Mars first?
In 1960, the Soviet Union was the first country to attempt a flyby of Mars with 1M (known in the West as Marsnik) but the mission was unsuccessful. The USA was the first nation to reach Mars successfully when Mariner 4 made a flyby of the Red Planet in July 1965.
What have we found on Mars?

Alas, there have been no reported sightings of little green men (yet), but what has been discovered on the Mars' surface is evidence of persistent liquid water, microbe-supporting chemistry, organic molecules, active methane and rocks. Lots of rocks.
What is the gravity on Mars?
As Mars is smaller than Earth, the effect of gravity is much weaker. That's great news if you want to lose weight quickly, because if you weighed 75kg on Earth, that would drop to just over 28kg on Mars. The formula is Weight on Mars = (Weight on Earth/Earth's gravity (9.81m/s2)) * Mars gravity (3.711m/s2).
Read more Mars reader Q&As:
- Could you throw a Frisbee on Mars?
- Could humans evolve to adapt to Mars?
- Would it be possible to fly a drone on Mars?
- What would astronauts eat on Mars?
What is between Mars and Jupiter?

Asteroids. Many, many asteroids. The majority of the Solar System's known asteroids lie between Mars and Jupiter, with between 1.1 and 1.9 million of them larger than a kilometre in diameter. There are millions more smaller ones, but are so spread out the distance between them is in the millions of kilometres.
What is the weather like on Mars?
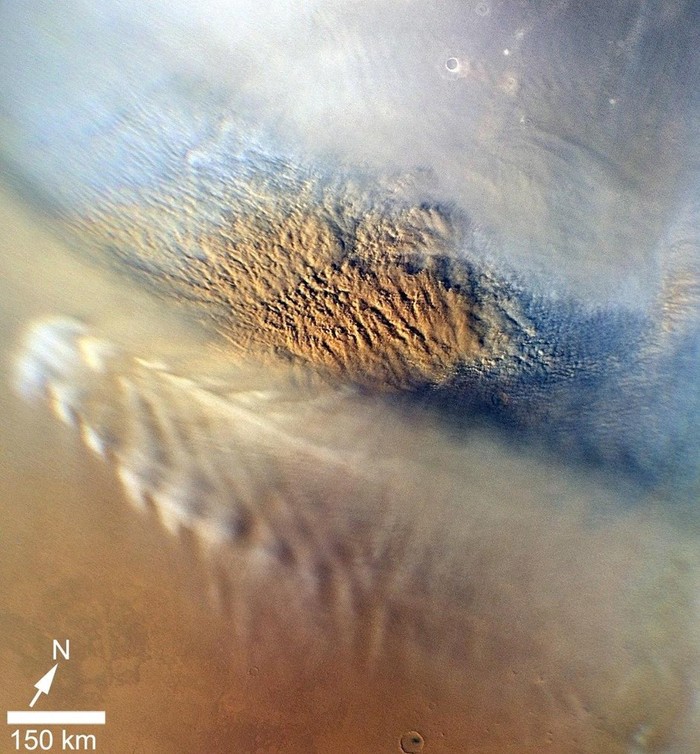
Despite the thin Mars atmosphere, the planet is still capable of clouds and weather. In fact, when it comes to wind, Mars has the biggest dust storms on all of the planets in the Solar System. If you want to know the weather right now, NASA's InSight rover is acting as an on-location weather reporter.
How many robots are on Mars?
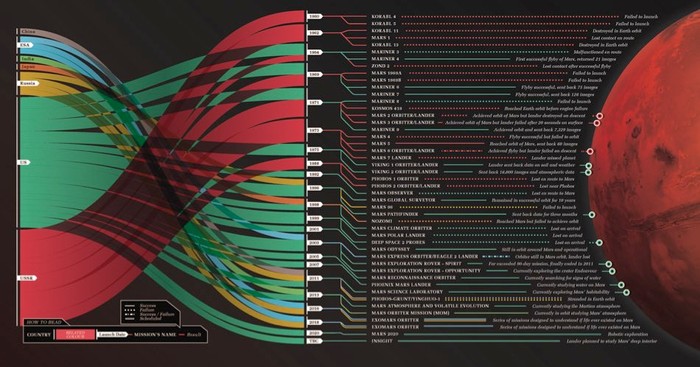
Mars is currently home to 16 robots, with more planned in the near future. Only two are currently operational, NASA's Curiosity rover and InSight lander, and four either crash-landed on the surface or broke up on entry. To date, Mars is the only known planet in the Universe to be entirely inhabited by robots.
What is Mars made of?
Below the surface, Mars is made up of a dense iron, nickel and sulphur core, and this is surrounded by a softer silicon and oxygen mantle. The planet's 50km-thick crust consists mainly of iron, magnesium, aluminium, calcium and potassium.
More like this
Where is Mars?
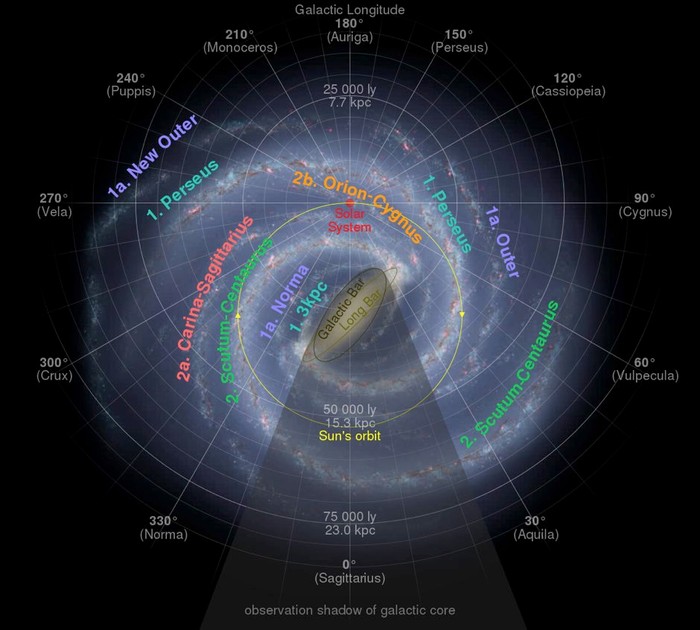
Mars can be found in space, but if you want to be more specific it's the fourth planet from the Sun in our Solar System, which itself is in the Orion-Cygnus Arm of the Milky Way. If you're into astronomical co-ordinates, it currently resides at RA 0h 58m 6s | Dec +2° 10′ 32″.
Why is Mars red?

The red colour of Mars comes from the high level of iron oxide in its regolith (surface material). However, why there is so much oxidised iron on a planet with virtually no oxygen in the atmosphere is still a mystery.
How hot is Mars?
Mars is not the sort of place you want to go on a summer holiday. After a months-long journey, you will be welcomed by a maximum temperature of around 20°C on the equator in summer. Down at the poles, Mars can get as cold as -125°C. The average temperature for the Red Planet is -63°C.
How big is Mars compared to Earth?
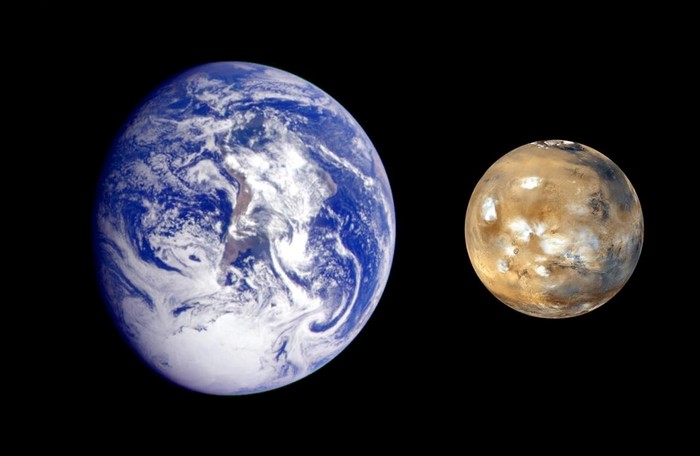

The diameter of Mars is 6,790km (4,220 miles), making it roughly half the size of Earth and twice as big as the Moon. This makes it the second-smallest planet in the Solar System.
What is the mass of Mars?
Although Earth is twice as big a Mars, it is around ten times heavier! So, we'll let you work out the mass of our home planet knowing that the red one pushes the scales at 6.42 x 1023 kilograms.
How old is Mars?
Mars is as old as the rest of the Solar System, making it a sprightly 4.6 billion years old.
How long is a year on Mars?
Mars takes 687 Earth days to orbit the Sun, which means it travels at a brisk 24km/s over its 9.55 AU journey (1 AU is about 150 million km, roughly the distance between the Earth and the Sun).
How did Mars lose its atmosphere?
Mars was once a warm, wet planet thanks to an atmosphere as thick as Earth's, but those days are long gone. Now it's a dusty old place due to atmospheric erosion, caused by a process known as 'sputtering'. This happens when ions carried by solar wind knock atoms out of the atmosphere and into space.
How long would it take to terraform Mars?

Terraforming means changing a planet's surface and atmosphere to be more like Earth's and therefore a suitable place to live. However, for it to work we need carbon dioxide, and Mars just doesn't have enough going spare. So until we sort that out, the answer is somewhere between a very, very long time to never.
How far is Mars from the Sun?
Mars has what is known as an eccentric orbit, which means it's not perfectly circular around the Sun. That means the distance between the two is always changing, but at their closest it is 206 million km, while its furthest is 249 million km. This averages out to around 229 million km.
What year was Mars discovered?

Mars is visible in the night sky with the naked eye, so it's impossible to say exactly when anybody first saw it. There are reports of it being sighted by the ancient Egyptians two millennia BCE. However, the first to spot it through a telescope was Galileo Galilei in 1610.
What type of planet is Mars?
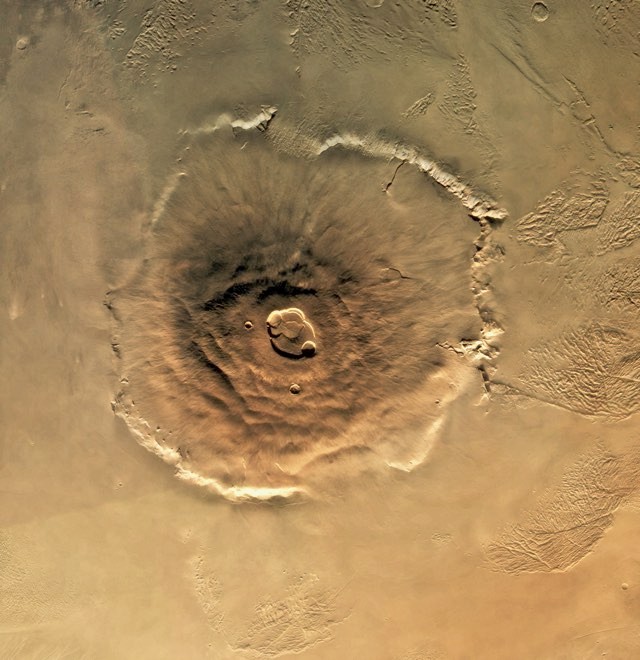

Mars is a rocky planet, covered in impact craters, mountains, volcanoes and deep canyons stretching thousands of miles. Olympus Mons is the tallest mountain in the Solar System, stretching 21,229m above the surface of the planet. That towers more than 12km above Mount Everest.
What is Mars named after?

The planet Mars was named after the Roman god of War. He was second only to the king of gods, Jupiter, and was a pretty bloodthirsty chap. That might go some way to explaining why the Red Planet was named after him. The animals most associated with him were the wolf and the woodpecker.
Which country landed on Mars first?
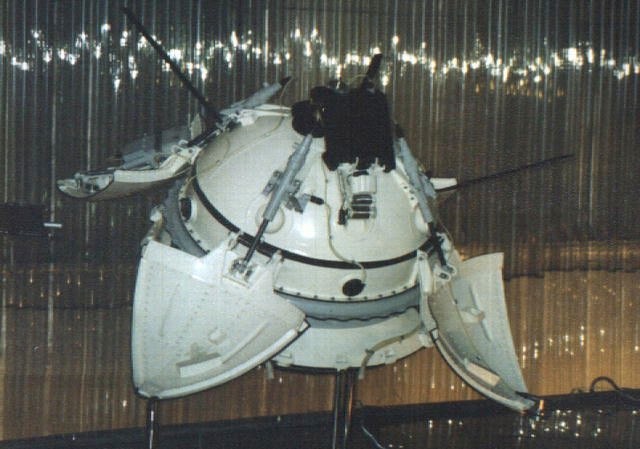

The USSR was the first country to place a human-made object on the planet's surface. The first attempt, Mars 2, crash-landed in November 1971, but less than a week later Mars 3 landed and remained operational for 14.5 seconds.
What colour is the sky on Mars?
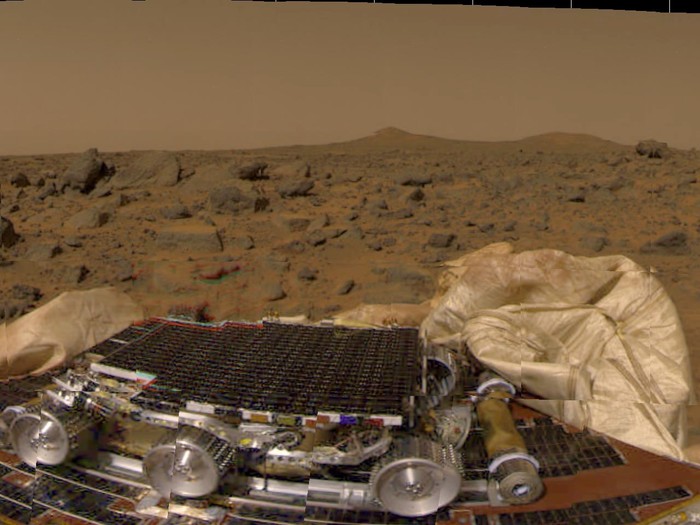

Weirdly, the colour of the sky on Mars is the opposite to Earth, being blue towards sunset and sunrise and reddish-pink during the day. This unusual daytime colour is caused by the vast amounts of dust containing Magnetite, an iron ore, suspended in the atmosphere.
Why are there no living cats on Mars?

Because Curiosity killed the cat. It's a joke, obvs... If you need a little more explanation, NASA's Mars Curiosity Rover landed on the Red Planet in 2012, presumably on top of any Martian felines. As of publication, there have been no reported sightings of cats on Mars and this band has a solid alibi.
Authors

Sponsored Deals

May Half Price Sale
- Save up to 52% when you subscribe to BBC Science Focus Magazine.
- Risk - free offer! Cancel at any time when you subscribe via Direct Debit.
- FREE UK delivery.
- Stay up to date with the latest developments in the worlds of science and technology.




